What is Fiber Optic Splitter?
Fiber optic splitter is a passive optical device that includes multiple input and output ends. It can divide the input optical signal into multiple output optical signals to meet the fiber optic access needs of multiple terminal devices. This type of device plays an important role in passive optical networks such as EPON, GPON, FTTH, etc.
Main Types of Fiber Optical Splitter
According to the manufacturing technology of fiber optic splitters, there are mainly two types of splitters: PLC splitter and FBT splitter.
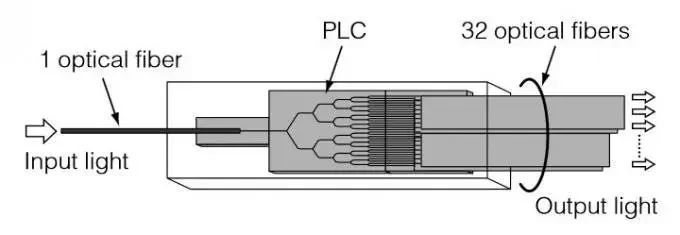
PLC splitter is a fiber splitter manufactured based on planar lightwave circuit technology, which can achieve even distribution of optical signals. The splitting ratio is usually 1 × N or 2 × N.
FBT splitter is made using traditional techniques by fusing and stretching two or multiple optical fibers to achieve fiber signal distribution. This type of splitter has a customizable splitting ratio as needed.
For more details: What is Fiber Optic Splitter and Types
How Does a Fiber Optic Splitter Work?
There are three main working principles of the fiber splitter:
1. Signal Input: The fiber splitter receives the optical signal from the upstream network node and enters the splitter through the input fiber.
2. Signal Distribution: Inside the splitter, according to the design structure and different optical technologies, the input optical signal is evenly or proportionally distributed to multiple output ports.
3. Signal Output: The distributed optical signal is transmitted to each receiving end through the output fiber.
Optical Fiber Splitter Application in FTTH
Optical fiber splitter is a core optical component in Passive Optical Network (PON) systems, and is widely used in Fiber To The Home (FTTH). The common architecture of FTTH consists of the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) located in the central office, the Optical Network Unit (ONU) at the user end, and the Optical Distribution Network (ODN) in between. Optical splitters are frequently used in ODN to help distribute the optical signals emitted by OLT to multiple user households. In FTTH networks, the distribution methods of fiber optical splitters are mainly divided into centralized splitting and cascaded splitting.
Centralized Splitting
Centralized splitting means that the optical splitter is centrally distributed in the fiber distribution box, one end connects directly to the OLT via a single fiber, while the other end connects to multiple ONTs at the user side through multiple fibers. The common splitting ratios of optical splitters are 1:32 or 1:64, which can be flexibly chosen based on user needs. This method can effectively utilize fiber resources, reduce costs, and enhance the manageability and ease of maintenance of the network, making it typically suitable for areas with a relatively concentrated and dense user population, such as urban or town areas.

Cascaded Splitting
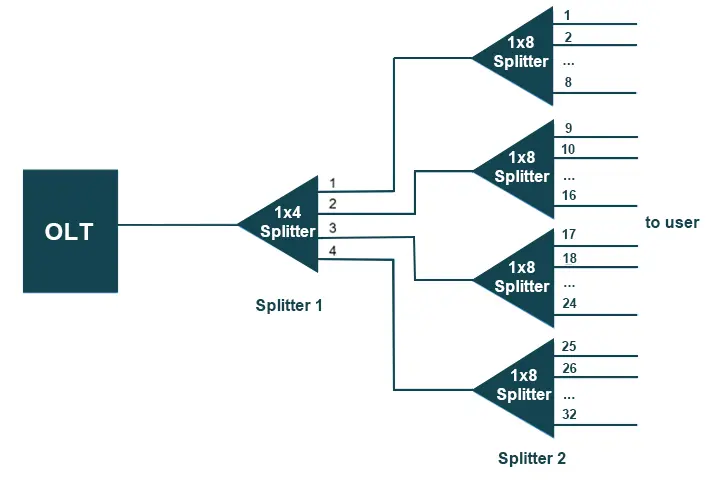
Cascaded splitting refers to the cascading configuration of optical splitters between the OLT and ONU, typically represented as “OLT → Splitter 1 → Splitter 2 → ONU”. In optical transmission links, a maximum of two stages of splitting are typically used to ensure effective management of optical loss, guarantee signal quality, and reduce costs. The optical signals are first distributed by the primary splitter, and then further distributed through the secondary splitter. The splitting ratio of the primary splitter is usually 1:4 or 1:8, while the secondary splitter typically has a splitting ratio of 1:8 or 1:16. This method allows for flexible selection of splitting ratios based on different user densities and needs, effectively reducing fiber and installation costs. It is typically suitable for areas with a dispersed user distribution, such as rural areas or small communities.
Contact Gcabling
Fiber optic splitters play a crucial role in PON by effectively distributing optical signals, reducing costs, and improving network scalability.
Gcabling has a professional product portfolio and technical team. Our fiber optic splitters use stable chips to control losses. The G657A1 fiber wire is better compatible with G652D and G657A2, supporting bend insensitive fibers with a minimum bending radius of 10mm. Additionally, our product has passed high and low temperature tests, enabling them to withstand environmental temperature changes. With outstanding performance, we can provide you with high-quality solutions.
If you have any questions about fiber optic splitters or need professional engineer assistance in selecting suitable products, please feel free to contact us at any time.

