What is Optical Fiber?
Optical fiber is a tool that utilizes the principle of total reflection of light in fibers made of glass or plastic to achieve light transmission, is widely used for transmitting optical signals in fields such as optical communication, sensing, medical treatment, data centers, etc., promoting the development of modern communication and information technology.
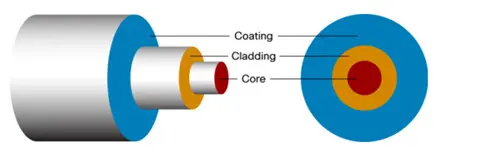
Structure of Optical Fibre
Optical fibre is composed of fiber core, cladding and coating.
Core
Fiber core is the central part of an optical fiber, which is made of high refractive index materials, usually glass or plastic. The diameter of the fiber core is usually only a few micrometers to tens of micrometers, which allows light to be transmitted within it. The smaller the diameter of the fiber core, the faster the transmission speed of light.
Cladding
The cladding is the outer layer of the fiber core, made of low refractive index materials, used to protect the fiber core and prevent light from escaping from the core.
Coating
Coating is a protective layer located outside the cladding, used to enhance the strength of optical fibers and provide mechanical protection, typically composed of polymer materials.
Types of Optical Fibers
According to the transmission mode, optical fibers can be divided into two types: single mode fibers and multimode fibers.
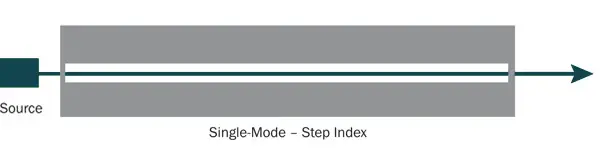
Single Mode Fiber
Single mode fiber has a small core and dispersion, the core diameter is usually 8-10 μm. It only allows optical signals to be transmitted in one mode, achieving lower attenuation and allowing signals to travel faster and farther.
Feature:
Small core diameter, low dispersion, providing higher bandwidth and transmission distance
Single mode transmission, low attenuation, high-quality signal transmission
Application:
Suitable for optical communication applications that require high speed, long distance, and high quality
Main Type of Single Mode Fibre:
The most popular single mode fibers in the current market are G652D, G657A1, and G657A2, and due to their identical physical dimensions, the fiber cables defined by these three standards can be fully compatible with each other.
G652D
G652D fiber is the most widely used optical fiber, also known as standard single mode fiber. It can be backwards compatible with early fiber versions and is suitable for most long-distance communication applications. But it is a rigid fiber with limited bending resistance, with a minimum bending radius of 30mm.
G657A1
G657A1 is a high-performance bend insensitive single mode fiber with better bending performance compared to G652D, with a minimum bending radius of 10mm without affecting performance.
G657A2
G657A2 is another type of bend insensitive single mode fiber with a minimum bending radius of 7.5mm, making it very suitable for applications in narrow spaces with high-density wiring.
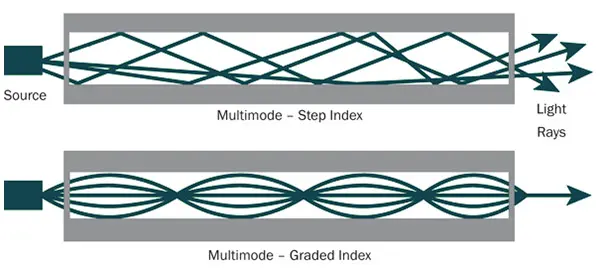
Multimode Fiber
Multimode fiber has a large core diameter and dispersion, with a core diameter of 50 or 62.5 μm, allowing hundreds of modes of transmission.
Feature:
Larger core diameter and dispersion than that of single mode fiber, lower bandwidth
Multiple transmission modes, large optical signal attenuation, relatively short transmission distance
Application:
Suitable for short distance and low speed data transmission applications
Main Type of Multimode Fibre:
Multimode fibers can be classified into OM1 fiber, OM2 fiber, OM3 fiber, OM4 fiber, and OM5 fiber.
OM1
OM1 is the earliest multimode fiber standard with a core size of 62.5 μm. It is usually equipped with an orange cable sheath, mainly used for short distance data transmission.
OM2
OM2 fiber is also an early type of multimode fiber, with a core size of 50 μm. Compared to OM1, it has lower transmission loss. Its cable sheath color is also orange.
OM3
OM3 fiber is a type of multimode fiber that supports high data transmission rates with a 50 μm core and aqua outer sheath. OM3 is laser optimized, with a data rate of 10GB/s at 850nm, transmission distance can reach 300m.
OM4
OM4 fiber is similar to OM3 fiber in that it is laser optimized with a core of 50 μm. The cable color is aqua (some manufacturers use violet), but it has better bandwidth performance and longer transmission distance. At a speed of 10GB/s at 850nm, the transmission distance of OM4 can reach 550m.
OM5
OM5 is the latest generation of multimode fiber, with a lime green cable jacket and a fiber size of 50/125 µm, fully compatible with OM3 and OM4. It can support four SWDM channels in windows ranging from 850nm to 953nm, aiming to meet the needs of high-speed and high-density data transmission.
Difference Between Single-mode Fiber and Multimode Fiber
| Parameter | Single Mode Fiber | Multimode Fiber |
| Core Diameter | 9-10 μm | 62.5/50 μm |
| Optical Source | Laser | LED |
| No. of Propagating Mode | One | Hundreds |
| Bandwidth | More | Less |
| Transmission Speed | Fast | Slow |
| Transmission Distance | Long | Short |
| Transmission Capactiy | Less | More |
| Attenuation | Less | More |
|
Modal Dispersion |
Small | Large |
|
Wavelength |
1310nm and 1550nm | 850nm and 1300nm |
|
Application Field |
Data center, long distance fiber optic communication | LAN, short-range optical communication, video surveillance |
Features of Fiber Optics
High Bandwidth
Optical fiber has high bandwidth characteristics, can provide higher data transmission rate and capacity.
Fast Transmission Speed, Long Transmission Distance
Compared with traditional copper cable, optical fibers can support higher transmission speed, as well as longer transmission distance, especially suitable for long-distance transmission.
Low Signal Loss
Optical fibre has the advantage of low transmission loss, the attenuation of the optical signal in the transmission process is small, ensuring efficient and high-quality transmission of signals over long distances.
Strong Anti-interference Ability
Optical fiber is a non-metallic dielectric material, the use of optical fiber as a conducting medium, not affected by electromagnetic interference.
Application of Optical Fibres
Fiber optics, due to its unique advantages and characteristics, has been widely used in many fields.