What is Single Mode Fiber?
Single mode fiber is a type of optical fiber that only allows optical signals to be transmitted in one mode. It has a smaller core than multimode fiber, with a core diameter generally between 8-10 μm, low dispersion, high bandwidth, and can achieve lower attenuation and longer transmission distance.
ITU-T (International Telecommunication Union) has defined different single mode fiber standards, including G.652, G.653, G.654, G.655, G.656, and G.657. Among them, the most widely used standards in the market are G652D, G657A1, and G657A2.
G652D vs G657A1 vs G657A2
G652D
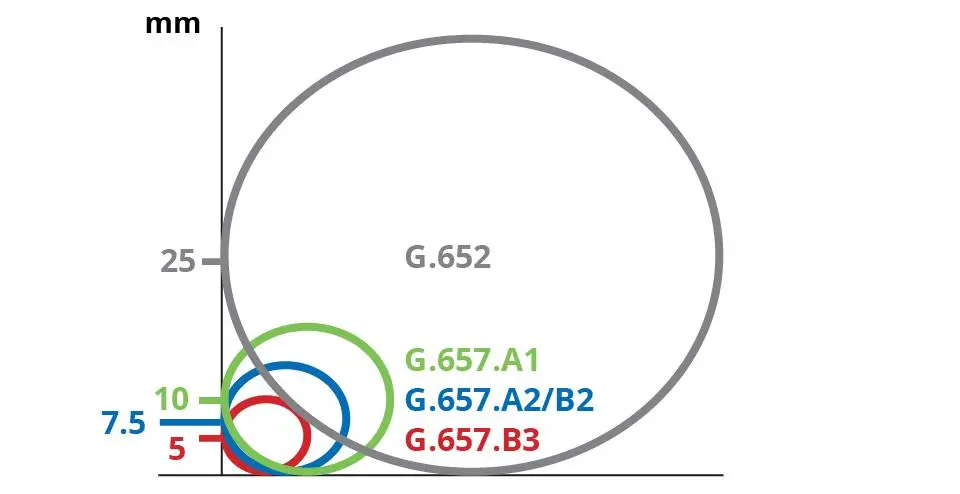
G652D fiber, also known as standard single mode fiber, has been used in the field of fiber optic communication for over 30 years and still dominates the market. It is currently the most widely used type of single mode fiber. G652D is a rigid fiber with limited bending resistance and a minimum bending radius of 30mm. Due to its backward compatibility, it can be more easily spliced with early G652 fibers, making it very popular in most long-distance communication applications.
G657A1
G657A1 is a single mode fiber type optimized for special application scenarios (higher fiber density cabling requirements), and belongs to the ITU-T G.657 standard. As a reliable high-performance bending insensitive single mode fiber, G657A1 has superior bending performance compared to G652D fiber, with a minimum bending radius of 10mm without affecting performance. This makes it very suitable for application in space constrained scenarios.
G657A2
G657A2 is another bending insensitive single mode fiber type under the ITU-T G.657 standard, which has further optimization compared to G657A1. Its main advantage lies in superior bending characteristics, with a minimum bending radius of 7.5mm. The emergence of G657A2 further optimizes the fiber performance for special scenarios, and the more professional small bend application fiber is very suitable for high-density wiring in narrow space applications.
FAQ about G652D & G657A1 & G657A2
Q: Are G.652.D, G.657.A1 and G.657.A2 compatible?
A: G.652.D, G.657.A1 and G.657.A2 have the same physical size, with an inner core diameter of 9μm and an outer core diameter of 125μm, so these three standard defined optical fibers can be fully compatible.
Q: What is the difference between G652D, G657A1 and G657A2?
A: Main difference between G652D, G657A1 and G657A2 lies in their bending radius. G652D has a larger bending radius, G657A2 has excellent bending performance and the smallest bending radius, while G657A1 has a bending radius between G652D and G657A2.
Q: How to choose between G652D, G657A1 and G657A2?
A: With good transmission performance and low transmission losses, G652D fiber is ideal for applications requiring long distance transmission and general communication environments. G657A1 and G657A2 have excellent bending performance, which is more suitable for some limited space and high bending requirements. In practical applications, the most suitable fiber type can be selected based on factors such as network layout, environmental requirements, and budget to ensure network performance and reliability.

